prehn test torsion testis|prehn test for testicular pain : exporting in multivariate analysis, a positive Prehn’s sign was predictive of testicular torsion, whereas fever, dysuria, high leucocyte counts in blood and/or urine, high blood C .
Resultado da processo seletivo pÚblico petrolina de goiÁs - go: processo seletivo simplificado itajÁ - go: saiba + concurso pÚblico chapadÃo do cÉu - go: .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 26 de nov. de 2021 · Espero que sim! Seguinte, hoje tenho um mega jogo de Naruto para te mostrar, isso mesmo, esse é um Mugen de Naruto com .
Prehn's sign (named after urologist Douglas T. Prehn) is a medical diagnostic indicator that was once believed to help determine whether the presenting testicular pain is caused by acute epididymitis or from testicular torsion. Although elevation of the scrotum when differentiating epididymitis from testicular torsion is of clinical value, Prehn's sign has been shown to be inferior to Doppler ultrasound to rule out testicular torsion.Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. A thorough history, the presence of a painful .
This video provides an overview of how to perform Prehn's test to elicit Prehn's sign in the context of testicular pain when testicular torsion is suspected.. The Prehn sign is not reliable for predicting torsion (relief of pain with testicle elevation). Torsion of the testicular appendages is more common and not dangerous. During . Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency with a 4-6hrs window from the onset of symptoms to salvage the testis before significant ischaemic damage occurs. Any suspected case warrants urgent surgical exploration of . in multivariate analysis, a positive Prehn’s sign was predictive of testicular torsion, whereas fever, dysuria, high leucocyte counts in blood and/or urine, high blood C .
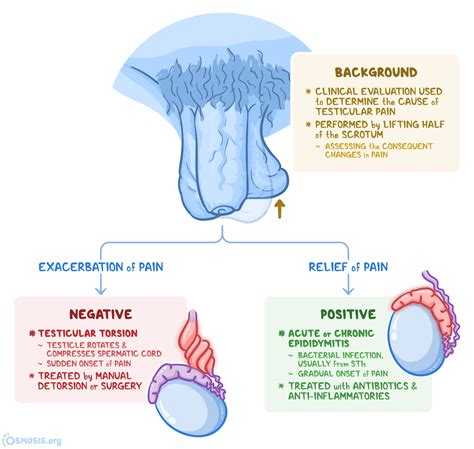
Testicular torsion classically presents with acute unilateral pain and swelling, abnormal cremasteric reflex, high position of the testicle, horizontal lie, and nausea/vomiting.Interpretation: Positive. Elevation of Scrotum relieves pain in Epididymitis. Does not offer relief in Testicular Torsion (elevation may worsen pain) V. Efficacy. Test Sensitivity: 91.3% Does not .Testicular torsion is described as the twisting of the spermatic cord resulting in acute pain and ischemia. This has a tendency to occur more frequently during adolescence and its cause is .
There is usually an associated hydrocoele with scrotal wall erythema; however, these are common examination findings of many diagnoses of acute scrotal pain. 7 If elevation of the scrotum does not relieve the pain (negative Prehn’s .Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. . (Prehn’s sign). 13. . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that requires multiple hemoclips and sessions of hemocoagulation . An absent cremasteric reflex is suggestive of testicular torsion (odds ratio = 7.8), whereas the reflex is preserved with epididymitis. 10 – 12 Torsion of the appendix testis is classically .Diagnosis dan tatalaksana cepat merupakan hal terpenting untuk menghindari kehilangan testis dan infertilitas di kemudian hari,. Kata Kunci: Korda spermatika, skrotum, testis, torsio. ABSTRACT Acute scrotal pain is a urological emergency with differential diagnoses of torsion of the testis (torsion of the spermatic cord), torsion of testicular
Prehn’s test is used to differentiate testicular pain caused by acute epididymitis and testicular torsion. The test involves elevating the testes to assess the impact on testicular pain . A reduction in testicular pain is associated with epididymitis . Torsion of the testicular appendages is considered the most common cause of acute scrotal pain in prepubertal children and may even be the single most prevalent cause of pediatric orchalgia.[1] Therefore, it should be included in the differential diagnosis for any male presenting with an acute scrotum, particularly in the pediatric age group.[1] Two testicular .
Loss of the cremasteric reflex is associated with testicular torsion, but always consider the clinical picture (plus any Doppler imaging) in addition to this clinical sign. Prehn’s Sign. Prehn’s Sign can be used to help differentiate between acute epididymitis and testicular torsion in those presenting with testicular pain.Testicular torsion must be considered in any patient who complains of acute scrotal pain and swelling. Torsion of the testis is a surgical emergency because the likelihood of testicular salvage . 1 Introduction2 Clinical Features3 Investigations4 Differential Diagnosis4.1 Testicular Torsion4.2 Torsion of Testicular and Epididymal Appendages4.3 Epididymitis4.4 Testicular Cancer4.5 Referred Pain5 Non-Urological Causes5.1 Henoch-Schoenlein Purpura5.2 Viral Orchitis6 Key Points Introduction Acute scrotal pain commonly presents on unilaterally . Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility. . A Prospective Comparison to Gold Standard Diagnostic Test Study. J Urol .
Torsio testis bisa dialami oleh laki-laki pada usia berapa pun, Torsio Testis. Torsio testis adalah kondisi ketika testis atau buah zakar terpelintir sehingga menimbulkan nyeri hebat pada testis. Torsio testis bisa dialami oleh laki-laki pada usia berapa pun, tetapi paling sering terjadi di usia kurang dari 25 tahun.B. Ultrasound evaluation with Doppler color flow Testicular torsion should be suspected in patients who complain of acute scrotal pain and swelling. Testicular viability is in jeopardy with delay in diagnosis, ultimately impacting the patient fertility. PPV 100% when 7 points; NPV 96% when <5 points; Our experts recommend against using the TWIST score to rule out torsion, however a score of 7 may warrant urgent urology consult with the aim of immediate surgical intervention without doppler ultrasound confirmation.The TWIST score requires further multicenter validation. Bottom line: “No .
the diagnostic accuracy of special tests for rotator cuff tear
Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 18. Previous testicular torsion. If you've had testicular pain that went away without treatment (intermittent torsion and detorsion), it's likely to occur again. The more frequent the bouts of pain, the higher the risk of testicular damage. Family history of testicular torsion.
prehn's test video
Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity. The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. .
Epididymitis is often confused with testicular torsion, use of the Prehn's sign may be helpful, but should always be followed with imaging to confirm the diagnosis. The ultrasound of the testicle with flow Doppler is still the preferred diagnostic treatment tool after a thorough history and physical examination has been completed. Most torsed . A normal reflex (i.e., ipsilateral cremasteric muscle contraction producing unilateral testis elevation) is present with epididymitis or orchitis and torsion of the appendix testis, but is almost .Spermatic cord: with thumb anteriorly and index finger posteriorly, feel neck of scrotum for spermatic cord (superior to testes, feels like string) Palpate for inguinal lymphadenopathy (infection/inflammation) Reflexes. Prehn’s test: if testicular pain is relieved by elevating the testes, suspect epididymitis; if not, suspect testicular torsion
the gold standard test for diagnosing and acl tear is
Thirty-three percent (14/42) of patients with testicular torsion had a positive Prehn’s sign at presentation, 19.0% (8/42) had no cremaster reflex, and 54.7% (23/42) had a retained testis unilaterally. Acute scrotum pain is defined as “the constellation of new-onset pain, swelling, and/or tenderness of the intrascrotal contents.” Patients may describe the onset of symptoms as rapidly as occurring within minutes or up to 1 to 2 days, dependent on the etiology. The acute scrotum is an umbrella term that includes a wide variety of unique disease processes. Rapid . Typically swollen and tender testis and/or lower abdominal tenderness [8] Nausea and vomiting; Abnormal position of the testis. Scrotal elevation (high-riding testis) Abnormal transverse position; Possible undescended testes (predisposes to testicular torsion) [9] Absent cremasteric reflex; Negative Prehn sign; In neonates. Possible absent testis Testicular torsion can occur at any age. Testicular torsion can occur at any age, but it is primarily associated with a bimodal distribution in the first year of life and in adolescence. Although exceedingly rare, there are case reports of testicular torsion occurring in .
Scrotal elevation relieves pain in epididymitis but not torsion. Study evidence showed (1): in multivariate analysis, a positive Prehn’s sign was predictive of testicular torsion, whereas fever, dysuria, high leucocyte counts in blood and/or urine, high blood C-reactive protein, and burning pain were predictive of genital/paragenital infectionScrotal and testicular masses can be broadly categorized into painful conditions, which include testicular torsion, torsion of the testicular appendage, and epididymitis, and painless conditions .Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become .Testicular torsion usually presents with an acute onset of diffuse unilateral testicular pain and tenderness of less than 6 h of duration. . which is a blue discoloration upon transillumination; this may be consistent with torsion of the appendix testis. The Prehn sign, a decrease in pain with physical lifting of the testicle, will relieve .
Failure of the ipsilateral testicle to rise during testing is indicative of testicular torsion. This test boasts a sensitivity ranging from 88% to 100%, . a decrease in pain with passive elevation of the testicle. A positive Prehn sign is common in cases of epididymitis and orchitis but will be negative, .
prehn's test osce
web16 horas atrás · Build up your collection of fighters, and carefully select whichever character from your arsenal suits your chosen battle the best to ensure you go undefeated! A .
prehn test torsion testis|prehn test for testicular pain